The previous article introduced the architecture and traffic flow of Neutron using the Linux Bridge plug-in under various scenarios. Over the next few days, I will introduce the architecture and traffic flow when using the OVS plug-in. In this first post, I will start by introducing Open vSwitch with Provider Networks.
Table of Contents
Open vSwitch: Provider Networks
Architecture
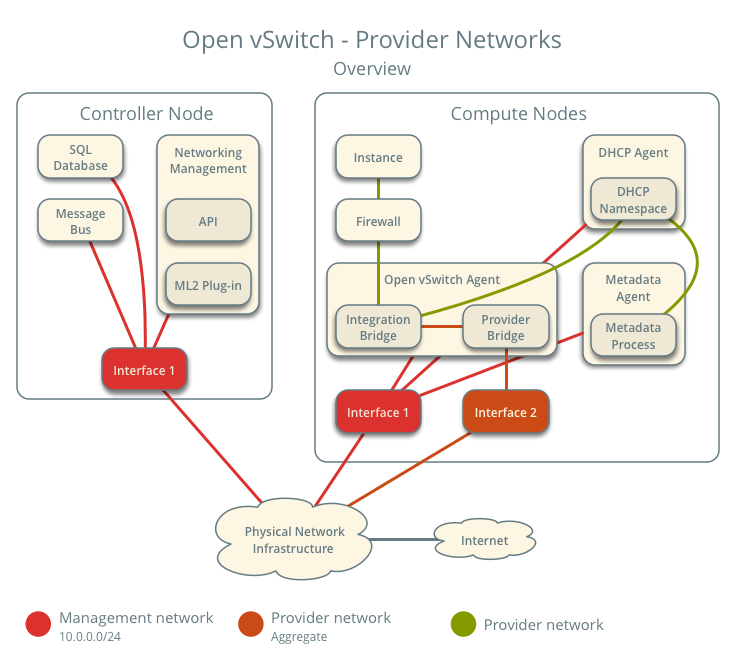
The diagram above provides an overview of the entire architecture under the Linux Bridge – Provider Networks setup. You can see which components run on the controller node and which run on the compute node.
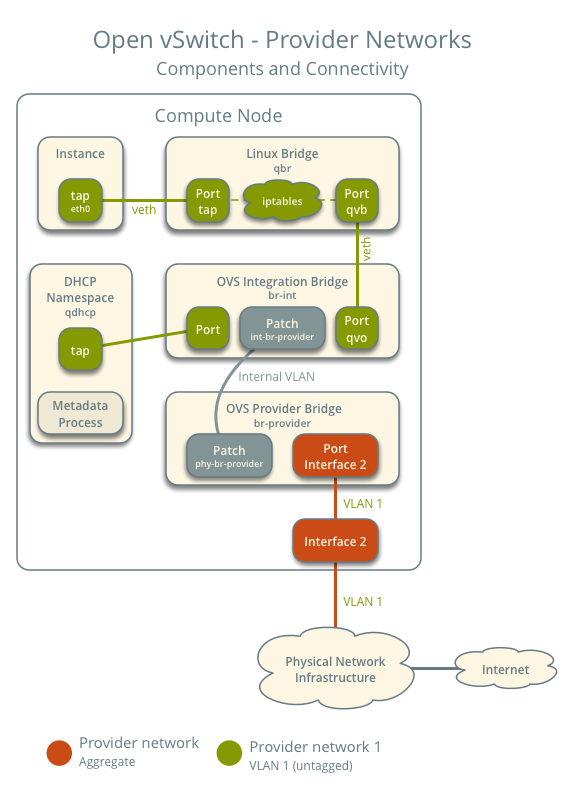
This diagram illustrates how components within a compute node are interconnected under a single provider network (untagged/flat). In this example, the Instance and the DHCP agent are on the same machine; however, in a real-world scenario, the DHCP agent might reside on a different compute node.
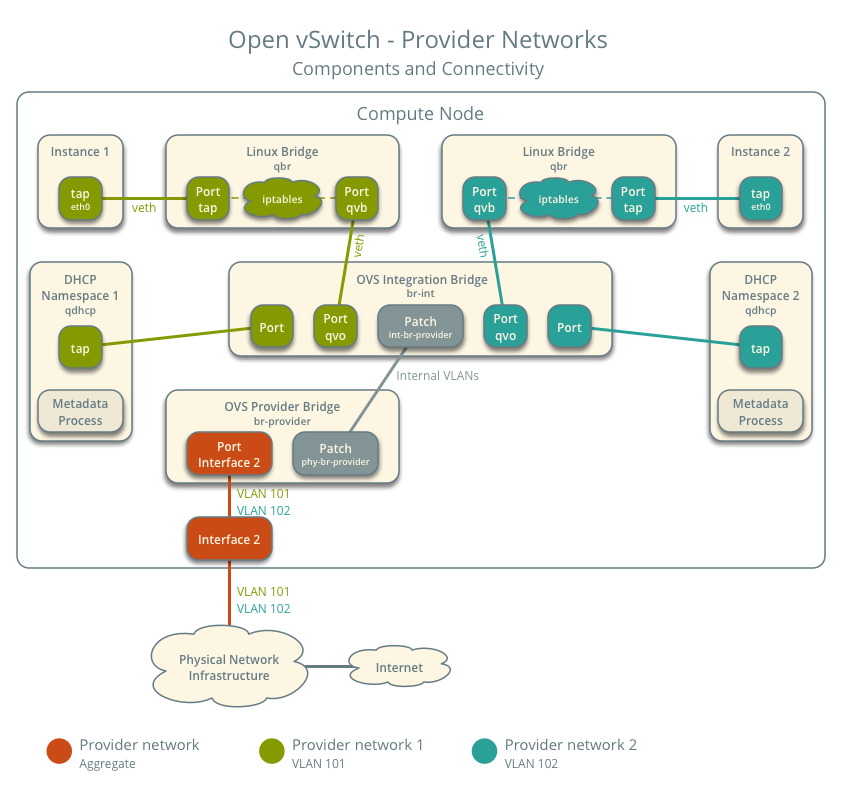
In scenarios with multiple Provider networks, each network uses the same OVS provider bridge and integration bridge but is isolated using different internal VLANs. The internal VLAN is typically different from the Neutron network VLAN.
Traffic Flow
This section will introduce how actual packets flow through the architecture under various conditions.
Architecture Configuration
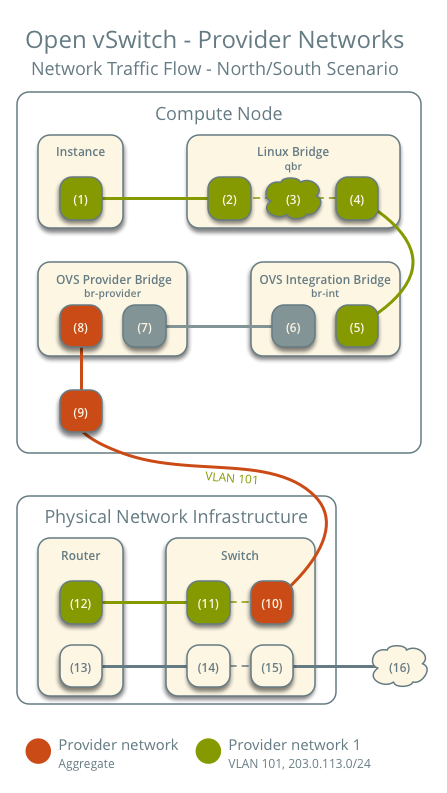
Below is our envisioned architecture, featuring two provider networks isolated via VLANs, each with one instance running on it.
- Provider Network 1 (VLAN)
- VLAN ID 101 (Tagged)
- IP address range 203.0.113.0/24
- Gateway (on the physical network)
- IP 203.0.113.1
- Provider Network 2 (VLAN)
- VLAN ID 102 (Tagged)
- IP address range 192.0.2.0/24
- Gateway
- IP 192.0.2.1
- Instance 1
- IP Address 203.0.113.101
- Instance 2
- IP 192.0.2.101
North-South Traffic
- Instance on compute node 1 using provider network 1
- The instance sends packets to the external network.
- The instance's network interface (1) sends packets to the instance port on the Linux bridge via a veth pair (2).
- On the Linux bridge, iptables (3) handles firewall rules and connection tracking.
- The OVS interface (4) on the Linux bridge sends packets to the OVS integration bridge security group interface (5) via a veth pair.
- The OVS integration bridge adds an internal VLAN tag to the packet.
- The OVS integration bridge's int-br-provider patch interface (6) sends packets to the OVS provider bridge's phy-br-provider patch interface (7).
- The OVS provider bridge replaces the internal VLAN tag with the actual provider network's VLAN tag 101.
- The provider network interface (8) on the OVS provider bridge sends packets to the physical network interface (9).
- The physical network interface sends packets to the switch (10) in the physical network infrastructure.
The subsequent part is consistent with general networking principles: packets are sent to the router and then forwarded out. The return path for packets follows the exact reverse process.
East-West Traffic 1: Instances on the same network
- Instance 1 is on compute node 1 and uses provider network 1.
- Instance 2 is on compute node 2 and uses provider network 1.
- Instance 1 sends packets to Instance 2.
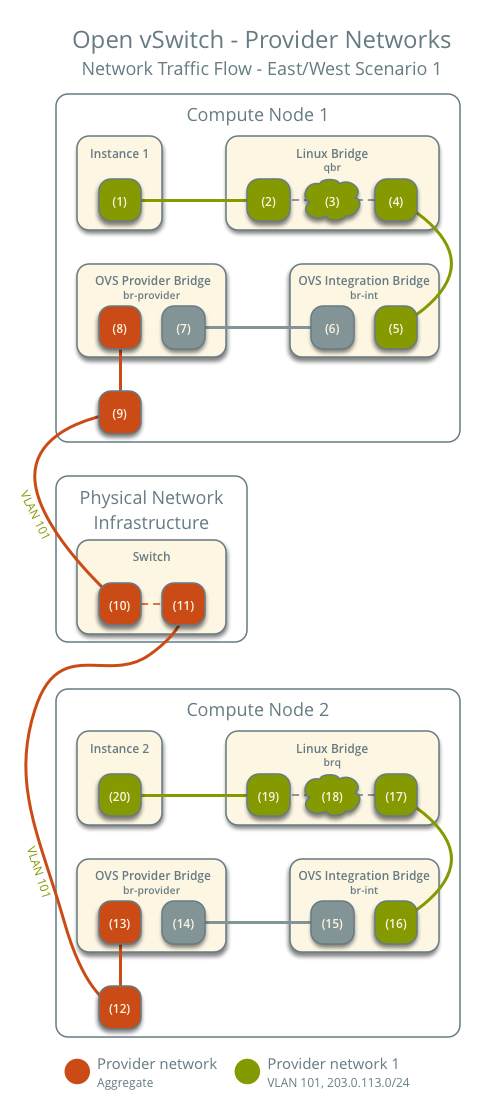 The preceding steps are exactly the same.
The preceding steps are exactly the same.
- The instance's network interface (1) sends packets to the instance port on the Linux bridge via a veth pair (2).
- On the Linux bridge, iptables (3) handles firewall rules and connection tracking.
- The OVS interface (4) on the Linux bridge sends packets to the OVS integration bridge security group interface (5) via a veth pair.
- The OVS integration bridge adds an internal VLAN tag to the packet.
- The OVS integration bridge's int-br-provider patch interface (6) sends packets to the OVS provider bridge's phy-br-provider patch interface (7).
- The OVS provider bridge replaces the internal VLAN tag with the actual provider network's VLAN tag 101.
- The provider network interface (8) on the OVS provider bridge sends packets to the physical network interface (9).
- The physical network interface sends packets to the switch (10) in the physical network infrastructure.
Within the physical network infrastructure:
- The switch sends packets from compute node 1 to compute node 2 (11).
After the packet reaches compute node 2:
- The physical network interface (12) sends packets to the provider network port (13) on the OVS provider bridge.
- The phy-br-provider patch port (14) on the OVS provider bridge sends the packet to the int-br-provider patch port (15) on the OVS integration bridge.
- The OVS integration bridge replaces VLAN tag 101 with an internal VLAN tag.
- The OVS integration bridge security group interface (16) sends the packet to the OVS interface (17) on the Linux bridge.
- On the Linux bridge, iptables (18) handles the firewall and connection tracking.
- The instance port (19) of the Linux bridge sends the packet to the instance's network interface (20) via a veth pair.
East-West Traffic 2: Instances on different networks
- Instance 1 is on compute node 1 and uses provider network 1.
- Instance 2 is on compute node 1 and uses provider network 2.
- Instance 1 sends packets to Instance 2.
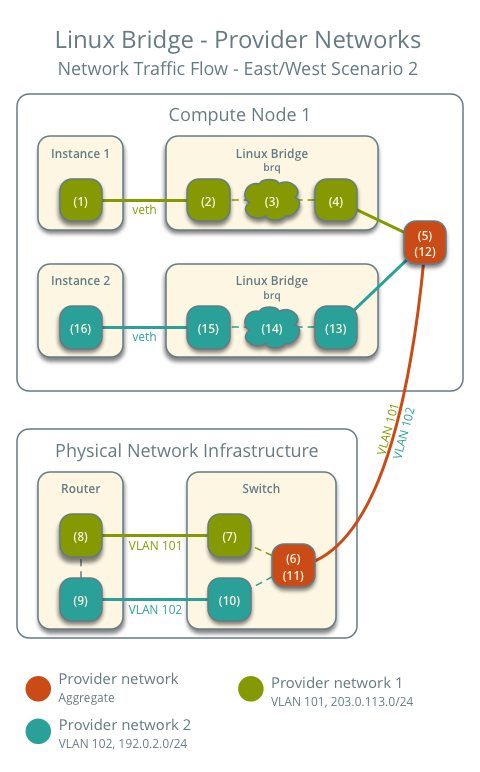 The initial process for sending the packet out is also the same.
The initial process for sending the packet out is also the same.
- The instance's network interface (1) sends packets to the instance port on the Linux bridge via a veth pair (2).
- On the Linux bridge, iptables (3) handles firewall rules and connection tracking.
- The OVS interface (4) on the Linux bridge sends packets to the OVS integration bridge security group interface (5) via a veth pair.
- The OVS integration bridge adds an internal VLAN tag to the packet.
- The OVS integration bridge's int-br-provider patch interface (6) sends packets to the OVS provider bridge's phy-br-provider patch interface (7).
- The OVS provider bridge replaces the internal VLAN tag with the actual provider network's VLAN tag 101.
- The provider network interface (8) on the OVS provider bridge sends packets to the physical network interface (9).
- The physical network interface sends packets to the switch (10) in the physical network infrastructure.
Within the physical network infrastructure:
- The switch removes VLAN tag 101 from the packet and sends it to the router (11).
- The router routes the packet from provider network 1 (12) to provider network 2 (13).
- The router sends the packet to the switch (14).
- The switch removes VLAN tag 102 from the packet and sends it to compute node 1 (15).
Returning to compute node 1:
- The physical network interface (16) sends the packet to the provider network port (17) on the OVS provider bridge.
- The phy-br-provider patch port (18) on the OVS provider bridge sends the packet to the int-br-provider patch port (19) on the OVS integration bridge.
- The OVS integration bridge replaces VLAN tag 102 with an internal VLAN tag.
- The OVS integration bridge security group interface (20) sends the packet to the OVS interface (21) on the Linux bridge.
- On the Linux bridge, iptables (22) handles the firewall and connection tracking.
- The instance port (23) of the Linux bridge sends packets to the instance's network interface (24) via a veth pair.
As you can see, aside from the different routing within the physical network infrastructure, the packet flow is very similar to sending packets to different instances on the same provider network. This concludes the overview of Open vSwitch Provider Network packet traffic under various scenarios.
Summary
This article introduces the architecture and packet flow under Open vSwitch – Provider Network. You will find that the overall concept is very similar to Linux Bridge – Provider Network, with the addition of the OVS integration/provider bridge in between. The next article will cover the architecture and packet flow using Open vSwitch – self-service network.
Copyright Notice: All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless otherwise stated.